ADVERTISEMENTS:
The minerals are classified into following groups:- 1. Quartz Group 2. Feldspar Group 3. Mica Group 4. Amphibole Group 5. Garnet Group 6. Kaolin 7. Carbonate Group 8. Sulphide Group 9. Oxide Group 10. Sulphate Group 11. Staurolite and Talc.
1. Quartz Group:
Form—Granular
Colour—(Varieties of quartz)
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Streak—Colourless
Lustre—Vitreous
Cleavage—Absent
Fracture—Conchoidal to uneven
Hardness—7 [High]
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Sp. Gr.—Low to Medium.
CC—SiO2
Occurrence:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Widely distributed all over India occurs Beach Sand River sand.
Uses:
1. Manufacture of glass, porcelain.
2. Flux in metallurgical operation.
3. Agates are used as Ornaments.
4. Amethysts are considered as semiprecious stone.
5. Pure quartz crystal shows piezoelectricity.
6. Quartz plates are used in controlling frequencies in radio circuits, radar, ultrasonic and multiple telephone lines.
7. Fibre quartz wires are frequently used for transmission of telephone messages. Each minute fibre wire can send large messages.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
8. Quartz is used in refractories.
9. Pure silica is used in ceramics.
10. Pure sand, free from impurities is used in manufacturing sand paper and abrasive cloth.
Varieties of Quartz:
1. Crystalline Varieties:
(a) Rock crystal or colourless quartz [Colourless, Transparent].
(b) Rosy quartz [Rose colour, Translucent].
(c) Milky quartz [Milk colour, Translucent].
(d) Gray quartz [Gray colour, Translucent].
(e) Amethyst [Purple or violet colour, Translucent].
(f)Smoky quartz [Smoke colour, Translucent].
(g) Orange quartz [Orange colour, Translucent].
(h) Green quartz [Green Translucent colour].
2. Cryptocrystalline Varieties:
(a) Chalcedony [Botryoidal, uniform light colour].
(b) Agate [Banded, zebra agate zebra colour].
(c) Jasper [Blood red colour].
(d) Chert [Brick red colour].
3. Amorphous Variety:
(a) Opal.
2. Feldspar Group:
3. Mica Group:
4. Amphibole Group:
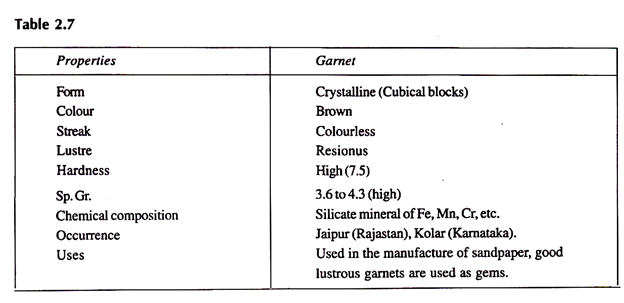
5. Garnet Group:
6. Kaolin (China Clay):
7. Carbonate Group:
8. Sulphide Group:
9. Oxide Group:
10. Sulphate Group:
11. Staurolite and Talc:
The Standard Format is to be advised while writing the description of minerals at the time of identification.
(A) Observation:
Name
Form
Colour
Streak
Diaphaneity
Lustre
Cleavage
Fracture
Hardness
Sp. Gr.
(B) Theoretical Information:
Chemical Composition (CC)
Crystal System (CS)
Indian Occurrences (IO)
Uses
(C) Note:
1. Silicate/Nonsilicate mineral.
2. Rock forming mineral/Ore forming mineral.
3. Belongs to the group.