ADVERTISEMENTS:
The term ‘orogeny’ was coined by the American geologist, G.K. Gilbert, in 1890 to describe the process of mountain building. The term was originally used by Gilbert to describe the fold mountain belts of the Alps and the Rockies.
According to the Oxford Dictionary of Geography the term ‘orogeny’ may be defined as tectonic “movements of the earth which involve the folding of sediments, faulting and metamorphism.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Two major types of orogeny are recognised: a cordilleran type in which geosynclinal deposits are severely deformed and one created by a continental collision when oceanic crust and sediment are trapped between two masses of continental crust.” The term can hardly be applied to mountains submerged in seas, because the submerged mountains originate through processes markedly distinct from those that created mountain systems like the Alps and the Rockies.
Classification of Mountains:
We may classify mountains based on various criteria.
1. On the basis of height:
(i) Low altitude mountains (700-1000 m)
(ii) Rough mountains (1000-1500 m)
(iii) Rugged mountains (1500-2000 m)
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(iv) High altitude mountains (above 2000 m)
2. On the basis of location:
(i) Continental mountains could be (a) coastal mountains; for example, the Rockies, the Appalachians, the Alpine mountain chains, the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats (India); or (b) inland mountains such as those found in the Vosges and the Black Forest (Europe), the Kunlun, Tienshan, Altai mountains of Asia, the Urals of Russia, the Aravallis, the Himalayas, the Satpura, and the Maikal of India.
(ii) Oceanic mountains are found on continental shelves and ocean floors. The height of the mountains is considered from the mean sea level. However, if considered from the ocean floor, some of the oceanic mountains will exceed the Himalayas in height. For example, Mauna Kea is about 9140 m from the sea bottom and thus is much higher than Mount Everest (8848 m).
3. On the basis of period of origin:
(i) Precambrian mountains belong to the geological time prior to the Cambrian period, a period that extended for more than 4000 million years. The rocks have been subjected to upheaval and metamorphosis. Traces of fossils are found in some unmetamorphosed rocks of Precambrian origin. Some of the examples are Laurentian Mountains, Algoman Mountains, Kilarnean mountains of Feno-Scandinavia, North-west highlands and Angleysey of Europe.
(ii) Caledonian mountains originated due to the great mountain-building movements and associated tectonic movements of the late Silurian and early Devonian periods. The mountains have a northeast-southwest alignment in the northwestern part of Europe. Caledonian mountains came into existence between approximately 430 million years and 380 million years ago. Examples are the mountains of Scotland, Ireland and Taconic mountains of the Appalachians, Aravallis, Mahadeo etc.
(iii) Hercynian mountains originated during the Upper Carboniferous to Permian Period in Europe. Some authors use the term Hercynian for the whole mountain systems belonging to central Europe, whereas others use the terms Altaides, Variscan to identify the same mountains system.
Hercynian mountains came into existence between approximately 340 million years and 225 million years ago. Some examples are the mountains of Iberian peninsula, Ireland, Spanish Messeta, Vosges and Black Forest, Variscan mountains of Europe and Altai, Sayan, Baikal Arcs, Khingan and Tien Shan mountains of Asia.
(iv) Alpine system had its origin in the Tertiary Period which consists of the Palaeocene, Eocene, Oligocene, Miocene and Pliocene epochs. The mountains were formed from about 65 million years to 7 million years ago. Examples are the Rockies of North America, the Alpine mountains of Europe, the Atlas mountains of north-western Africa, the Himalayas of the Indian sub-continent, mountains radiating from Pamir knot like Pauntic, Taurus, Elburz, Zagros and Kunlun etc.
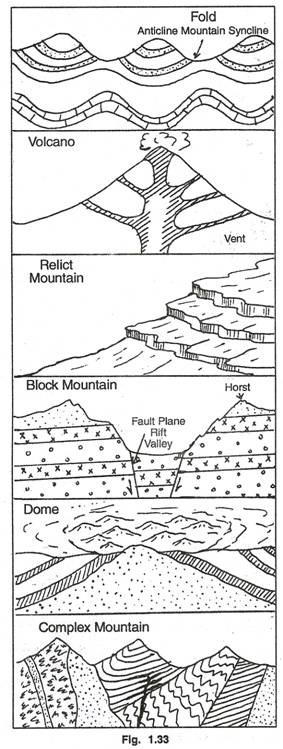
4. On the basis of mode of origin:
(i) Original or Tectonic mountains are the product of tectonic forces i.e., endogenetic forces originating from deep layers of the earth. The tectonic mountains may be categoried into fold mountains, block mountains and volcanic mountains.
(ii) Circum-erosional or Relict or Residual mountains are the remnants of old fold mountains derived as a result of denudation.